Current UTC Time
Click to see the current time in any location globally.
You can find the current UTC time displayed above. However, it's important to understand that UTC does not account for daylight saving time or other seasonal changes. Therefore, depending on your location and local regulations, the actual time may vary.
To ensure precise tracking of global events, such as airline schedules or financial transactions, many institutions heavily rely on UTC as a consistent reference point. It facilitates uniformity across borders and eliminates confusion caused by varying regional times. For accurate conversions between UTC and local time, you can use this powerful search engine to find the current time in any location globally.
UTC serves as a standard for synchronizing clocks worldwide, ranging from highly accurate atomic clocks that measure seconds to everyday devices like smartphones and laptops. The widespread adoption of UTC guarantees unambiguous communication between different locations across the globe.
While not as widely recognized as some other global standards, UTC plays an indispensable role in our daily lives, often unnoticed by most individuals. As our world continues to witness increasing global interconnectivity, the significance of UTC will only become more evident in the years to come.
What is UTC?
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) serves as the world's standard time, providing a reference for time coordination globally. It is based on atomic clocks and ensures a reliable and accurate measurement of time. Unlike Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and other time standards, UTC remains constant and does not change due to seasonal variations.
The concept of UTC was introduced in 1960 by the International Radio Consultative Committee (CCIR) to replace GMT as the international timekeeping standard. It was officially adopted by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 1967 and has gained widespread acceptance since then.
UTC operates through a network of atomic clocks located in different parts of the world. These clocks are precisely synchronized with each other to ensure consistent time readings. The high accuracy of these clocks guarantees that regardless of your location, you can rely on UTC as a reliable reference for time measurement.
To account for the gradual slowing of Earth's rotation over centuries, occasional leap seconds are added to the calendar year, aligning it with astronomical events such as solstices and equinoxes.
UTC plays a crucial role in modern communication, serving as a universal reference point for tracking global activities across regions and countries simultaneously.
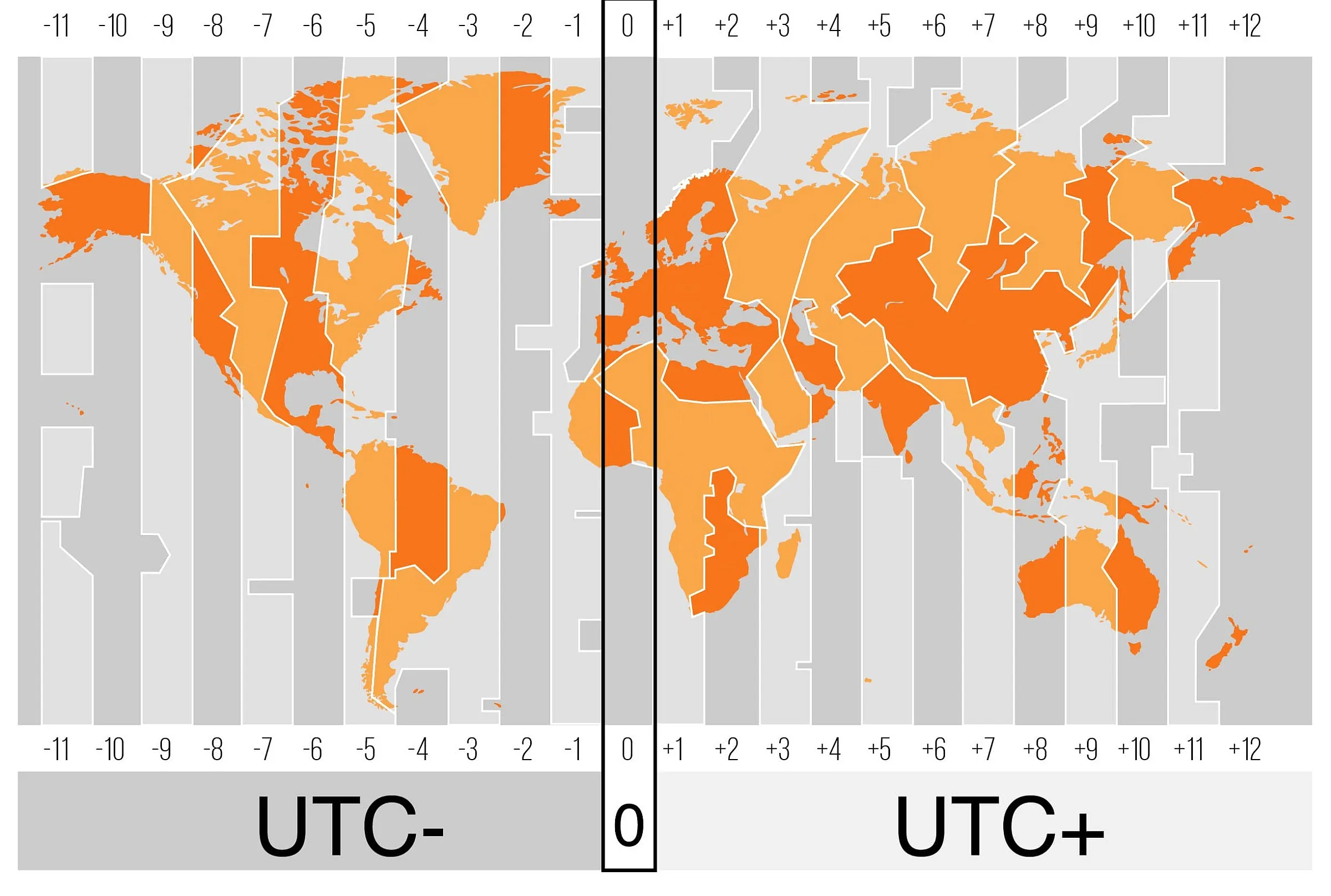
Time Zone Map showing UTC Deviation in Hours
The Time Zone Map displays regions with varying deviations from UTC, represented by shades of yellow and orange. The bottom and top sections of the map indicate the deviation from UTC in hours.
The UTC offset refers to the variance, expressed in hours and minutes, between Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and a specific place and date. Typically, it is represented in one of the following formats: ±[hh]:[mm], ±[hh][mm], or ±[hh]. For instance, if the time in question is one hour ahead of UTC, such as during winter in Berlin, the UTC offset would be indicated as "+01:00", "+0100", or simply "+01".
The History of UTC
The history of UTC can be traced back to the late 19th century when the expansion of telegraph lines across continents necessitated a standardized time system. Prior to that, each country utilized its own local time based on the position of the sun at noon in their respective capital cities.
However, as global communication and transportation became more prevalent, the need for a universal standard became evident to avoid confusion and errors. Consequently, the International Meridian Conference took place in Washington D.C. in 1884, where delegates from around the world reached an agreement on defining longitude and establishing time zones.
Moving ahead to 1960, the introduction of atomic clocks revolutionized timekeeping with unprecedented accuracy. This breakthrough prompted the development of UTC as a means of synchronizing all clocks globally, regardless of their location or technology.
Presently, UTC is widely recognized and accepted as the primary reference time scale for various applications such as scientific research, satellite navigation systems, air traffic control, financial transactions, and much more. Its significance cannot be overstated in our interconnected world, where precise and consistent time measurement is of utmost importance.
The History of UTC
Today, UTC is extensively utilized by various industries and organizations worldwide, playing a critical role in coordinating international communications, transportation, finance, and scientific research.
One of the primary applications of UTC lies in global communication systems, including satellites and internet networks. These systems rely on precise timing to ensure accurate data transmission and synchronization across devices spanning different time zones. UTC serves as the standard reference for achieving this synchronization.
The aviation industry heavily depends on UTC for flight coordination. Pilots utilize UTC to schedule flights, air traffic controllers rely on it to manage air traffic across multiple regions simultaneously, and airports utilize it for accurate scheduling of takeoffs and landings.
Beyond aviation, UTC finds usage in financial services where synchronized global time is crucial for trading transactions. Scientific researchers rely on precise timestamps based on UTC for experiments, observations, and data analysis. Military operations benefit from UTC for coordinating activities across units situated in different continents. Healthcare providers rely on accurate timekeeping based on UTC for patient care records management, among other applications.
The widespread adoption of UTC globally has resulted in substantial benefits by enhancing coordination and accuracy across various industries. It continues to play a pivotal role in enabling seamless and synchronized operations in an increasingly interconnected world.
Advantages of Using UTC
The utilization of UTC as the world's time standard offers numerous advantages. One of the primary benefits is the elimination of confusion and the assurance of accuracy across different time zones. By having a universal reference point, global communication and coordination become significantly easier and more efficient.
UTC enables precise scheduling and synchronization of events, such as international flights or live broadcasts. It facilitates streamlined operations for businesses operating across multiple countries, promoting international trade and reducing administrative complexities.
Another advantage of UTC is its impartiality. Unlike regional time standards such as GMT or EST, UTC is free from cultural or political biases. This makes it an ideal choice for global organizations operating in diverse locations worldwide, ensuring equitable and standardized time measurement. You can leverage the accurate timekeeping based on UTC to avoid discrepancies and foster efficient global collaboration.
Moreover, UTC can contribute to energy conservation in buildings equipped with automated lighting systems. These systems can be programmed based on the latitude and longitude coordinates of the location, utilizing UTC for sunrise and sunset information. This eliminates the need to adjust for daylight saving changes every six months, leading to more efficient energy usage.
The widespread adoption of UTC has brought significant benefits to our modern society and continues to play a crucial role in facilitating international communication and coordination. It serves as a reliable and neutral time standard, fostering efficiency, consistency, and global collaboration.
Disadvantages of Using UTC
While UTC has numerous advantages, it is true that there are some disadvantages associated with using this time standard. It can lead to confusion for individuals accustomed to using local time zones. Scheduling meetings or coordinating activities across different locations can be challenging, requiring additional effort to convert between UTC and local times. However, by familiarizing yourself with UTC and using reliable time conversion tools, you can overcome these challenges and ensure efficient coordination across time zones.
Another drawback is that UTC does not consider daylight saving time or regional variations, leading to discrepancies during certain periods. The difference between UTC and local time zones may vary by an hour or more, causing potential confusion or disruption.
For individuals working night shifts or irregular hours, the 24-hour clock format of UTC can pose difficulties in converting between local times and UTC. This can make it more complex to manage schedules and coordinate activities effectively.
While most modern computer systems and applications support UTC, there may still be legacy systems that do not fully recognize this standard. This can create issues when synchronizing data across different platforms or networks, requiring additional efforts for compatibility.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of using UTC as a global time standard typically outweigh the drawbacks. Its widespread adoption and the benefits it brings in terms of coordination, communication, and consistency make it an indispensable tool in our interconnected world.
Did you know about UTC?
UTC, which stands for Coordinated Universal Time, serves as the global 24-hour time standard that forms the basis for civil time worldwide. The offset of each time zone is determined in relation to UTC, indicated as either UTC- or UTC+, along with the corresponding number of hours and minutes.
Essentially, UTC is derived from mean solar time at the prime meridian passing through Greenwich, UK. With every 15 degrees of longitude traveled east or west, the mean solar time adjusts by 1 hour. To convert mean solar time to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), two time components are combined: International Atomic Time (TAI), measured by atomic clocks, and Universal Time (UT1), which represents the actual duration of a day on Earth.
In principle, the UTC offsets employed by countries should align with their respective local mean solar time. However, various geographical and political factors often lead to distortions in time zone boundaries.
Further interesting facts about UTC:
- UTC stands for Coordinated Universal Time and is a time standard used worldwide, not a time zone.
- It combines two components: International Atomic Time (TAI), which provides the exact speed for atomic clocks, and Universal Time (UT1), which refers to the Earth's rotation.
- Universal Time (UT) was established in 1884 at the International Meridian Conference, and it served as the basis for the 24-hour time zone system.
- In 1960, the concept of UTC was formalized by the International Radio Consultative Committee, and it was officially adopted in 1967.
- Leap seconds were introduced in 1972 to account for the slight variations between UTC and the Earth's rotation.
- Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is now a time zone used by a few countries in Africa and Western Europe, while UTC remains the global time standard.
Remember, UTC keeps our world synchronized and ensures consistent timekeeping across borders!